Introduction: Robotics for Elderly Care in Japan
In response to its aging demographic, Japan has become a global leader in developing and deploying robotics to address the challenges of elderly care. As the nation faces the rapid increase in the elderly population, the conventional methods of care are no longer enough to meet the rising demands. Japan is increasingly turning to robotics to improve care for seniors, not only enhancing their quality of life but also supporting overwhelmed caregivers. With a population where more than 28% are 65 years old or older, robotics is playing a crucial role in reshaping elderly care. The country is investing in robots that can assist in daily living, provide companionship, and support medical needs. This article delves deeper into Japan’s integration of robotics into elderly care, exploring how these technologies are changing lives and what the future holds.
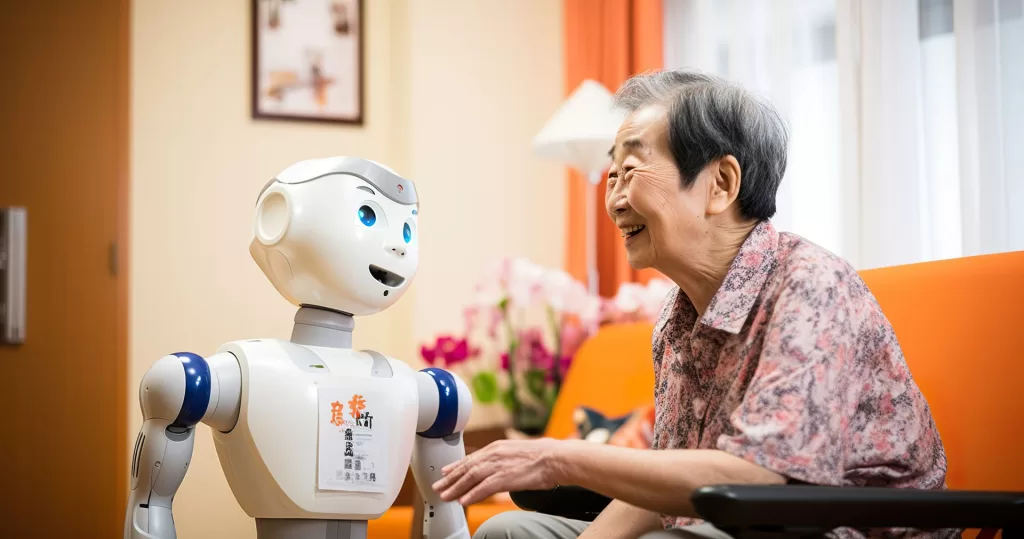
The Growing Need for Elderly Care in Japan
Japan is experiencing one of the most significant demographic shifts in the world. With a birthrate that continues to decline and life expectancy on the rise, Japan’s aging population has reached a critical point. According to the United Nations, by 2030, Japan will have the highest proportion of elderly individuals in the world. This presents a massive challenge to the country’s healthcare infrastructure, and the labor shortages in the caregiving sector only exacerbate the problem. The traditional model of elderly care, largely dependent on human labor, is becoming increasingly unsustainable. Robots and other advanced technologies are emerging as an essential part of the solution to this crisis.
Japan’s Robotics Industry: A Hub of Innovation
Japan has long been a leader in robotics innovation, and its robotics industry is uniquely positioned to tackle the challenges of elderly care. The country’s culture of technological advancement, coupled with government support and investments, has led to the development of various robotic systems designed specifically for elderly care. These robots are a blend of engineering, artificial intelligence (AI), and healthcare solutions, transforming how Japan’s elderly receive care.
By 2020, the Japanese government announced its initiative to integrate robotics more extensively into elder care as part of the “Robot Revolution Initiative.” This initiative is a national effort to encourage the development of robots that can assist with daily care tasks, increase independence for seniors, and reduce the reliance on human caregivers. The goal is not only to meet the current demands but also to create scalable and sustainable solutions for the future.
Robots for Daily Assistance: Promoting Independence
A key focus of Japan’s robotic innovations for elderly care is improving daily living for seniors. Robots designed for physical assistance enable elderly individuals to maintain a sense of autonomy while reducing the physical strain on human caregivers. These robots range from humanoid machines to compact mobile devices, all created with the specific goal of providing assistance to seniors with limited mobility or physical disabilities.
One of the most notable examples of these assistive robots is the Robear, developed by RIKEN and Sumitomo Riko Company. The Robear was designed to lift elderly patients who are unable to move on their own, such as when transferring from a bed to a wheelchair. Unlike human caregivers, who are prone to injury from lifting heavy patients, Robear is equipped with sensors and AI systems that allow it to perform these tasks safely and efficiently. With its gentle, bear-like design, Robear has also been praised for its comforting appearance, helping reduce anxiety in patients who may feel uncomfortable around traditional medical equipment.
Another remarkable innovation is Paro, a robot designed to offer therapeutic companionship to elderly individuals with dementia. Paro is a soft, baby seal-like robot that responds to touch and sound, calming patients with dementia and reducing symptoms of loneliness. This type of robot has been increasingly used in Japan’s nursing homes, where it provides emotional support to elderly individuals who may not be able to form meaningful human connections. The soothing effects of Paro have made it a favorite among healthcare professionals, who note its positive impact on the mental well-being of patients.
Robotics in Healthcare: Advancing Medical Care for Seniors
Robotics isn’t limited to physical assistance – it’s also transforming the medical care available to elderly individuals. Medical robots are now being used in hospitals, homes, and other care facilities to help monitor and manage the health of senior citizens. Japan is at the forefront of this innovation, incorporating AI and robotic technology into its healthcare infrastructure.
A key development in this field is telemedicine robots. These robots allow elderly individuals to consult with medical professionals remotely, eliminating the need to travel for routine check-ups. With the use of video and AI-powered diagnostics, these robots can conduct health assessments and relay the data to healthcare providers, making it easier for elderly people, especially those in rural areas, to receive medical attention.
Another breakthrough is the Hybrid Assistive Limb (HAL), a robotic exoskeleton developed by Cyberdyne, which has been used to assist the elderly with mobility. HAL is designed to support movement by reading the bio-signals from the user’s body and enhancing their motion. For elderly individuals who struggle with walking or movement due to conditions like arthritis or muscle weakness, HAL has proven to be a game-changer, enabling them to walk more freely and maintain a higher level of independence.
Integrating Artificial Intelligence and Big Data for Elderly Care
In addition to physical assistance and healthcare support, artificial intelligence (AI) and big data are also being incorporated into Japan’s elderly care ecosystem. AI-powered robots are capable of performing routine health checks, monitoring vital signs, and even predicting health problems before they become critical. For example, AI-driven robots can detect signs of dementia, alerting caregivers early so that treatment can begin before the condition worsens. These robots are equipped with sophisticated algorithms that learn from their interactions with patients, continuously improving their ability to offer personalized care.
Big data plays a vital role in the management of elderly health. With the vast amount of health data collected from sensors and wearable devices, caregivers can make more informed decisions about treatment. By analyzing health trends and patient histories, data-driven insights can help caregivers provide better care. In Japan, the use of AI and big data analytics is expected to revolutionize the elderly care sector, offering personalized, precise, and proactive care for aging populations.
The Economic Impact of Robotics on Elderly Care
The economic implications of robotics for elderly care are profound. As Japan faces an aging population, the cost of providing long-term care is expected to rise exponentially. Robotics offers a solution to this problem by reducing the need for human caregivers and lowering healthcare costs. Robotic systems can work 24/7 without the need for breaks, offering a more consistent and cost-effective approach to elderly care.
Additionally, the rise of robotics in elderly care has created new job opportunities in the tech and healthcare sectors. Japan is not only addressing the caregiving shortage but is also establishing itself as a leader in the global robotics market, exporting its innovations worldwide. As demand for robotic care solutions grows, the economic impact will continue to expand, benefiting both the healthcare system and the nation’s economy as a whole.
Timeline of Robotics in Elderly Care: Key Milestones
- 2005: The Japanese government recognizes the need for robotics to assist in elderly care, funding research in robotic technology as part of its efforts to address the challenges of an aging population.
- 2010: The introduction of the RIBA (Robot for Interactive Body Assistance) marks a major milestone in robotic care. This robot is designed to assist with lifting and transferring elderly patients.
- 2015: The development of Paro, a therapeutic robot for dementia patients, becomes widely adopted in nursing homes and elderly care facilities across Japan.
- 2017: The launch of HAL (Hybrid Assistive Limb), a robotic exoskeleton designed to help elderly individuals regain mobility, ushers in a new era of mobility assistance technology.
- 2020: Japan’s government announces the integration of AI and robotics into elderly care nationwide, enhancing the scope of robotic applications and accessibility for senior citizens.
- 2023: The deployment of robotic hospital assistants, capable of carrying out tasks such as delivering medicine and checking vital signs, demonstrates how robotics is reshaping elderly healthcare.
Expert Opinions on Robotics for Elderly Care
Dr. Hiroshi Ishiguro, a renowned roboticist and director of the Intelligent Robotics Laboratory at Osaka University, emphasizes, “Robots are designed to complement human caregivers, not replace them. The future of elderly care relies on creating a harmonious interaction between advanced robotics and the human touch.”
Dr. Akihiko Noguchi, an expert in AI applications for healthcare, adds, “AI-driven robots offer great promise in elderly care. By monitoring vital signs, predicting health issues, and providing assistance with daily tasks, they can significantly enhance the quality of life for seniors while alleviating caregiver stress.”
Conclusion: The Future of Elderly Care is Robotic
As Japan continues to grapple with its aging population, robotics is proving to be a transformative force in elderly care. With innovative solutions like assistive robots, telemedicine devices, and AI-powered healthcare technologies, Japan is setting the stage for a future where elderly care is more efficient, affordable, and humane. These technological advancements not only help elderly individuals live more independently but also ensure that caregivers can provide higher-quality care with less physical and emotional strain. Japan’s robotics-driven approach is paving the way for the future of elderly care, providing a model that other nations can adopt as they face similar demographic challenges. The future is bright, and robotics will play a crucial role in ensuring that aging populations receive the care they deserve.
📚 Take Your Trading And Financial Skills to the Next Level!
If you enjoyed this post, dive deeper with our Profitable Trader Series—a step-by-step guide to mastering the stock market.
- Stock Market 101: Profits with Candlesticks
- Stock Market 201: Profits with Chart Patterns
- Stock Market 301: Advanced Trade Sheets
Start your journey now!
👉 Explore the Series Here
For Regular News and Updates Follow – Sentinel eGazette
FAQs
Q1: How is Japan using robotics to help with elderly care?
A1: Japan is incorporating robotics into elderly care by using robots for physical assistance, healthcare support, and emotional companionship. Robots like Robear help lift patients, while Paro provides comfort to those with dementia. Additionally, AI-powered robots are used for monitoring health remotely.
Q2: Are robots replacing human caregivers in Japan?
A2: Robots are not replacing human caregivers but are intended to assist them. By handling routine tasks like patient lifting and health monitoring, robots reduce the physical strain on human caregivers, enabling them to focus on more complex and personal care needs.
Q3: What are the most popular robots in Japan for elderly care?
A3: Some of the most popular robots include Robear for lifting patients, HAL (Hybrid Assistive Limb) for mobility, and Paro, a therapeutic robot that helps with dementia care by providing emotional support.
Q4: How has AI technology enhanced elderly care in Japan?
A4: AI technology is used to analyze health data and predict potential issues before they become serious. AI-powered robots are able to monitor vital signs, detect changes in health conditions, and alert caregivers to any irregularities, improving the efficiency and quality of care.
Q5: What is the economic impact of robotics on elderly care in Japan?
A5: Robotics is reducing long-term caregiving costs by minimizing the need for human caregivers and offering 24/7 support. It also opens up new job opportunities in the tech and healthcare sectors, contributing to Japan’s economy while addressing labor shortages in elder care.