Introduction: Local vs National Government in South Korea
South Korea, a country known for its rapid modernization and democratic governance, operates with a well-organized system that separates the functions of its local and national governments. This separation allows for more efficient management and ensures that both national priorities and regional needs are addressed. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of the roles and responsibilities of local and national governments in South Korea, comparing their powers and functions in great detail.
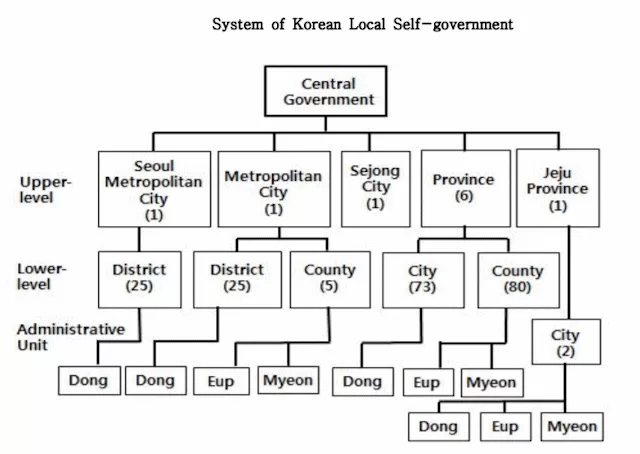
Government Structure in South Korea: An Overview
South Korea’s government is divided into two main levels: the national government and the local governments. Each level of government has distinct roles, with the national government handling large-scale national matters, and local governments managing issues that are more region-specific. The constitution of South Korea provides the framework for this system of governance, which ensures the efficient functioning of the country by balancing power and authority between the national and local levels.
The national government is composed of three branches: the executive, the legislature, and the judiciary. These branches operate within a structure that guarantees checks and balances. Local governments, on the other hand, operate within provinces, metropolitan cities, and smaller administrative units like districts and towns.
The Role of the National Government in South Korea
The national government holds significant authority over major policy decisions affecting the country as a whole. The three branches of the national government are designed to handle different aspects of governance:
- Executive Branch: The President, who serves a single five-year term, leads the executive branch. The President is responsible for formulating and executing domestic and foreign policies, ensuring national security, and managing the country’s defense. Additionally, the executive branch oversees the implementation of laws and manages the overall functioning of the government.
- Legislative Branch: The National Assembly is a unicameral body consisting of 300 members. This body is tasked with passing laws, approving national budgets, and overseeing the work of the executive. Members of the National Assembly play a crucial role in creating the legislative framework that guides the country’s operations.
- Judicial Branch: South Korea’s judicial system ensures the rule of law by interpreting laws, resolving disputes, and protecting the constitutional rights of its citizens. The judiciary is independent, with the Constitutional Court having the authority to rule on constitutional issues, and the Supreme Court overseeing legal matters at the highest level.
The national government’s key responsibilities include:
- National Defense and Security: The national government is responsible for ensuring the country’s security, especially due to the ongoing tension with North Korea. This involves overseeing the military, implementing defense strategies, and managing national security policies.
- Foreign Relations: The national government handles all diplomatic affairs, including formulating foreign policies, managing trade relations, negotiating international agreements, and representing South Korea on the global stage.
- Economic Development: The government plays a vital role in shaping economic policy, regulating industries, and fostering economic growth. Policies regarding taxation, employment, and national financial management are crafted by the national government.
- Healthcare and Social Welfare: South Korea has a highly efficient healthcare system, and the national government is responsible for managing public health policies, health insurance, and social welfare programs.
- Education: The national government establishes educational standards, curriculum, and funding for public schools and universities. It ensures that all citizens have access to education and that there are no disparities in educational opportunities across regions.
The Role of Local Governments in South Korea
Local governments in South Korea are responsible for governing their respective regions, ensuring that the needs of local populations are met. These local authorities are organized into provinces, metropolitan cities, and municipalities (districts, towns, and villages). The autonomy of local governments is enshrined in the constitution, which ensures that regional concerns are handled more directly by local elected officials.
Key responsibilities of local governments include:
- Local Administration: Local governments oversee the implementation of public services within their regions. This includes waste management, local law enforcement, and ensuring that local residents have access to essential services like water, electricity, and healthcare.
- Urban Planning and Infrastructure: Local governments are in charge of urban development, which includes constructing and maintaining roads, parks, public buildings, and other essential infrastructure. They also manage zoning and land-use planning to ensure that development is sustainable and that communities are well-connected.
- Education: While the national government establishes educational policies, local governments manage the administration of public schools and are responsible for ensuring that local schools are properly funded and equipped. They also oversee the hiring of teachers and other school staff at the local level.
- Public Health: Local governments play a key role in managing public health at the community level. This includes overseeing health centers, running vaccination programs, and managing initiatives related to disease prevention and public health awareness.
- Social Welfare: Local authorities provide social services, including support for low-income families, elderly care, and assistance for vulnerable populations. They implement national welfare policies at the community level and ensure that citizens receive the necessary support.
- Cultural Affairs: Local governments are involved in promoting local culture and organizing events such as festivals, local arts programs, and other cultural activities. They manage cultural centers and promote the preservation of cultural heritage.
Key Differences Between Local and National Government in South Korea
While both the national and local governments in South Korea share the goal of improving the well-being of the citizens, their functions and responsibilities are distinct:
- Scope of Jurisdiction: The national government’s policies affect the entire country, covering defense, foreign affairs, and national economic strategies. Local governments, on the other hand, are concerned with issues specific to their regions, such as local administration, public services, and community development.
- Policy Making and Implementation: The national government formulates policies that apply to all regions, while local governments implement those policies at the local level and may create additional policies that are relevant to their specific area.
- Budget and Financial Management: The national government controls most of the nation’s financial resources, but it allocates funds to local governments to support regional projects. Local governments also generate their own revenue through taxes, but they typically have smaller budgets compared to the national government.
- Public Services: The national government provides public services that must meet national standards, while local governments focus on tailoring services to the unique needs of their communities.
- Decision-Making Process: National government decisions have a broader impact, while local governments focus on localized decision-making. National laws and policies are enforced uniformly across the country, but local regulations may vary from one region to another.
The Timeline of Evolution: Local and National Government Cooperation
The evolution of South Korea’s governance system has seen increased cooperation between national and local governments. Over the decades, local governments have gained more authority in areas such as education, social welfare, and urban planning. The decentralization process has allowed local governments to better address the needs of their communities while still adhering to national laws and policies.
In recent years, there have been discussions around further decentralization of power, with local governments seeking more autonomy in decision-making and financial management. This trend reflects the desire for a more responsive government that can adapt to the rapidly changing needs of South Korean society.
Experts’ Opinions on South Korea’s Local vs National Government Dynamics
Dr. Jae-Min Kim, a professor of political science at Seoul National University, shared his insights on the current balance of power between local and national governments in South Korea. According to Dr. Kim, “The relationship between local and national governments in South Korea is characterized by a delicate balance. Local governments must navigate national policies while addressing regional needs, and this can sometimes lead to friction. However, the ongoing process of decentralization is helping to align local priorities with national goals.”
Professor Young-Hee Park, an expert on public administration at Yonsei University, emphasizes that “While local governments have gained more autonomy over the years, there remains a significant need for cooperation with the national government. National policies often influence local implementation, and collaboration ensures that local developments align with national strategic goals.”
Conclusion: A Balanced System of Governance
South Korea’s system of governance, with its clear distinctions between local and national responsibilities, allows for effective management at all levels. The national government oversees issues of national importance, such as defense, foreign relations, and economic policies, while local governments focus on community development, public services, and regional governance. This system has proven to be effective, fostering national unity while ensuring that regional concerns are addressed.
As South Korea continues to develop and face new challenges, the cooperation between local and national governments will remain crucial in promoting the country’s progress and maintaining social cohesion. This balance between national and local powers ensures that South Korea remains responsive to both the needs of its citizens and the demands of the global stage.
📚 Take Your Trading And Financial Skills to the Next Level!
If you enjoyed this post, dive deeper with our Profitable Trader Series—a step-by-step guide to mastering the stock market.
- Stock Market 101: Profits with Candlesticks
- Stock Market 201: Profits with Chart Patterns
- Stock Market 301: Advanced Trade Sheets
Start your journey now!
👉 Explore the Series Here
For Regular News and Updates Follow – Sentinel eGazette
FAQs:
Q1: What is the difference between local and national governments in South Korea?
A1: The primary difference lies in jurisdiction. National government handles countrywide matters such as defense, foreign policy, and economic strategies. In contrast, local governments are responsible for regional issues like urban planning, public services, and local welfare.
Q2: How does the local government contribute to South Korea’s urban development?
A2: Local governments in South Korea are tasked with urban planning, which includes the construction and maintenance of infrastructure, roads, and public buildings. They also manage zoning laws and oversee sustainable development in their regions.
Q3: What role does the national government play in South Korea’s education system?
A3: The national government sets educational standards, curriculum, and allocates funding to public schools. It ensures that educational opportunities are available across all regions and that there are no disparities in access to education.
Q4: How does the national government manage South Korea’s defense?
A4: The national government, through its executive branch, is responsible for formulating defense strategies and managing the military. This includes ensuring national security, particularly in light of the tension with North Korea.
Q5: How has decentralization affected South Korea’s local governance?
A5: The decentralization process has given local governments more autonomy in decision-making. This has led to more responsive governance at the regional level, enabling local authorities to address community-specific issues more effectively.