India and China, two of the world’s most populous countries, have experienced remarkable economic growth over the past few decades. However, there are growing concerns that they might be at risk of falling into the middle-income trap. This concept, coined by economists, describes a situation where a country’s growth slows after reaching middle-income levels, preventing it from becoming a high-income economy. In this article, we will explore the challenges India and China face, the factors contributing to the middle-income trap, and potential strategies to sustain their economic growth.
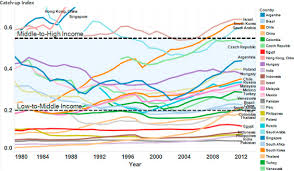
Understanding the Middle-Income Trap
The middle-income trap occurs when countries experience rapid growth and transition from low to middle-income status but then stagnate and fail to achieve high-income levels. This phenomenon is often attributed to several factors, including a reliance on cheap labor, limited innovation, inadequate education systems, and poor governance. Countries caught in this trap struggle to compete with both low-wage economies and advanced high-income nations.
Economic Growth in India and China: A Timeline
1990s – Early 2000s: Economic Reforms and Rapid Growth
- India and China implemented significant economic reforms, liberalizing their markets and attracting foreign investment. These reforms led to rapid industrialization, increased exports, and substantial GDP growth.
2000s – 2010s: Sustained Growth and Development
- Both countries continued to experience robust economic growth. China emerged as the world’s manufacturing hub, while India’s services sector boomed. This period saw significant poverty reduction and improvements in living standards.
2010s – Present: Signs of Slowing Growth
- Recently, both economies have shown signs of slowing growth. Structural challenges, rising labor costs, and external economic pressures have raised concerns about their ability to sustain past growth rates.
Challenges Faced by India and China
Structural Economic Issues
India and China both face structural economic challenges that could impede their growth. In India, issues such as inadequate infrastructure, bureaucratic inefficiencies, and a complex regulatory environment hinder business operations. For China, the transition from an investment-driven economy to a consumption-driven one poses significant challenges. The aging population and shrinking labor force further exacerbate these issues.
Innovation and Technology
Innovation and technological advancements are crucial for countries to move beyond middle-income status. While China has made significant strides in technology and innovation, it still faces challenges in intellectual property protection and fostering a truly innovative culture. India, on the other hand, has a vibrant tech sector but needs to invest more in research and development to drive innovation across various industries.
Education and Skills Development
A well-educated and skilled workforce is essential for sustained economic growth. India and China need to address gaps in their education systems to ensure their labor force can adapt to changing economic demands. In India, improving the quality of primary and secondary education is critical, while China needs to focus on higher education reforms and vocational training.
Strategies to Overcome the Middle-Income Trap
Enhancing Innovation and Technology
To avoid the middle-income trap, India and China must prioritize innovation and technology. This involves investing in research and development, fostering a culture of creativity, and improving intellectual property protection. Collaborations between universities, research institutions, and industries can drive technological advancements and create high-value industries.
Strengthening Education Systems
Improving education systems is vital for developing a skilled workforce. India should focus on enhancing the quality of primary and secondary education, ensuring access to education in rural areas, and promoting vocational training. China should continue to reform higher education, encourage critical thinking, and support lifelong learning initiatives.
Economic Reforms and Governance
Both countries need to implement economic reforms to create a more conducive business environment. For India, simplifying regulatory frameworks, reducing bureaucratic red tape, and investing in infrastructure are key priorities. China should focus on deepening market reforms, reducing state intervention, and promoting fair competition.
Conclusion
India and China stand at a critical juncture in their economic development. While they have achieved significant progress, the risk of falling into the middle-income trap looms large. By addressing structural challenges, investing in innovation and technology, and strengthening education systems, they can pave the way for sustained growth and avoid the pitfalls of economic stagnation. The journey ahead is complex, but with strategic planning and effective governance, both nations can achieve high-income status and secure a prosperous future for their citizens.
For Regular News and Updates Follow – Sentinel eGazette
Sources:
FAQs
1. What is the middle-income trap?
The middle-income trap refers to a situation where countries experience rapid growth and transition from low to middle-income levels but then stagnate and fail to achieve high-income status due to various structural challenges.
2. How can India and China avoid the middle-income trap?
India and China can avoid the middle-income trap by prioritizing innovation and technology, strengthening education systems, and implementing economic reforms to create a more conducive business environment.
3. What are the main challenges faced by India and China in achieving high-income status?
The main challenges include structural economic issues, gaps in innovation and technology, and inadequacies in their education systems.
4. Why is innovation important for avoiding the middle-income trap?
Innovation is crucial as it drives technological advancements, creates high-value industries, and enables countries to compete globally, moving beyond low-wage, low-skill economic activities.
5. What role does education play in economic growth?
Education is vital for developing a skilled workforce that can adapt to changing economic demands, drive innovation, and support sustainable economic growth.