The ongoing Gaza conflict has reached another critical juncture as Hamas has formally rejected the new ceasefire conditions proposed in the recent US-led talks. This development not only complicates the situation in Gaza but also raises significant questions about the future of peace negotiations in the region. This article provides a comprehensive analysis of the current state of affairs, the reasons behind Hamas’s rejection, and the potential implications for the broader Middle East.
Current Situation in Gaza: A Detailed Overview
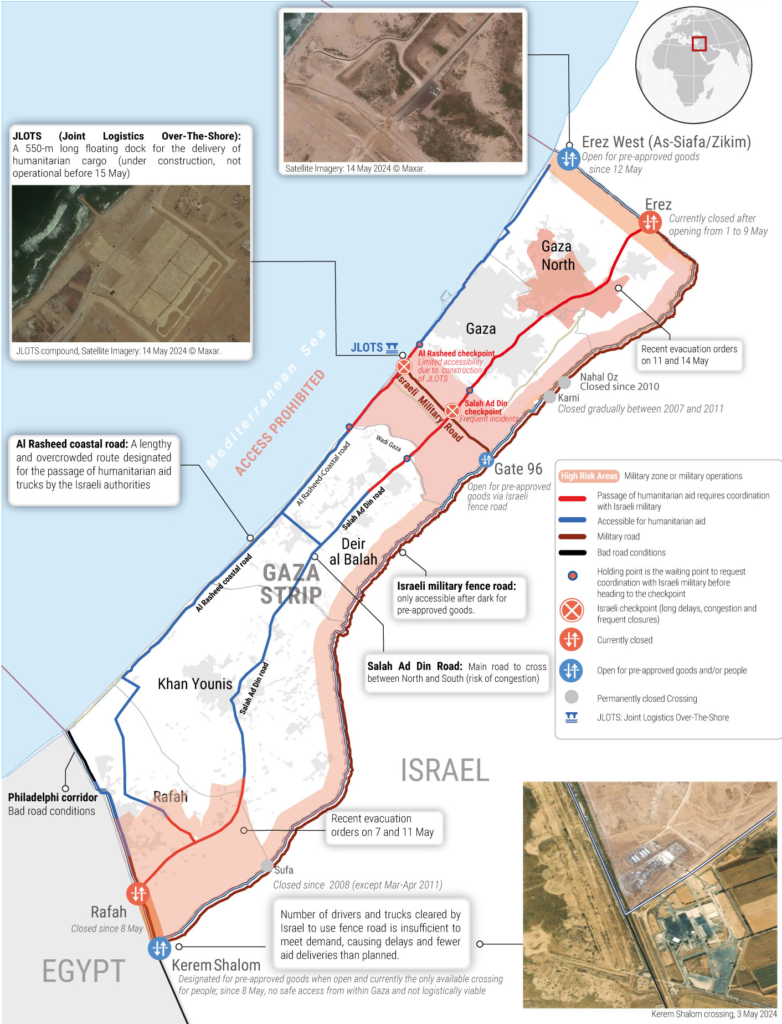
The Gaza Strip, home to over two million Palestinians, remains one of the most volatile regions in the world. The recent escalation in violence has seen an increase in military clashes between Hamas and Israeli forces. According to reports from the United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA), the conflict has resulted in over 1,000 casualties and extensive damage to infrastructure in Gaza.
The humanitarian situation in Gaza has worsened with disruptions in essential services such as water, electricity, and medical care. Efforts to mediate the conflict have been hampered by the complex geopolitical landscape and the entrenched positions of the involved parties.
US-Led Ceasefire Talks: An Overview of Proposed Conditions
In a bid to de-escalate the conflict, the United States, in collaboration with international partners, initiated a new round of ceasefire talks in Cairo, Egypt. Key proposals included:
- Humanitarian Aid Access: The plan aimed to facilitate the unrestricted flow of humanitarian aid into Gaza. This included the provision of food, medical supplies, and other essential resources to the affected population.
- Ceasefire Monitoring: A comprehensive monitoring mechanism was proposed to ensure that both sides adhere to the ceasefire terms. This involved international observers and the use of technology to track compliance.
- Economic Reconstruction: The proposal outlined a framework for the reconstruction of Gaza’s infrastructure, including the rebuilding of schools, hospitals, and residential areas that have been damaged during the conflict.
Despite these proposals, the talks faced significant challenges. The parties involved struggled to reach a consensus on critical issues, leading to a stalemate.
Hamas’s Rejection: Reasons and Implications
Hamas’s rejection of the ceasefire conditions is rooted in several core issues:
- Perceived Bias in Conditions: Hamas has criticized the new conditions as being one-sided and failing to address key grievances, such as the blockade of Gaza. They argue that the proposed measures do not provide sufficient relief or address their security concerns.
- Dissatisfaction with Previous Agreements: Historical context plays a role in Hamas’s stance. Previous ceasefire agreements have often been breached or inadequately implemented, leading to a lack of trust in the current proposal.
- Internal Political Pressures: Hamas faces pressure from various factions within Gaza, including political rivals and militant groups, who are skeptical of any agreement perceived as disadvantageous. This internal dissent complicates Hamas’s ability to negotiate effectively.
The rejection of the conditions poses significant risks, including the potential for further escalation of violence and a prolonged humanitarian crisis in Gaza.
International Community’s Response: Reactions and Actions
The international community has reacted with concern to Hamas’s rejection. Key responses include:
- United Nations: UN Secretary-General António Guterres has called for both sides to return to the negotiating table and emphasized the urgent need for humanitarian assistance. He noted that continued violence will only exacerbate the suffering of civilians.
- European Union: The EU has expressed disappointment and urged for renewed dialogue. High Representative Josep Borrell stated that a sustainable peace agreement must address the underlying causes of the conflict, including economic and humanitarian issues.
- Regional Players: Countries such as Egypt and Jordan have called for calm and continued diplomatic efforts. Egyptian President Abdel Fattah el-Sisi has offered to mediate further talks to bridge the gap between the conflicting parties.
Potential Pathways to Peace: Exploring Solutions
Several potential pathways could lead to a resolution of the conflict:
- Revised Negotiation Framework: A revised set of conditions that addresses both Hamas’s and Israel’s core concerns could pave the way for renewed negotiations. This would require flexibility and concessions from all parties involved.
- Increased Diplomatic Engagement: Enhanced involvement from major international powers, including the United States, European Union, and regional stakeholders, might help facilitate a more balanced agreement.
- Humanitarian Focus: Prioritizing humanitarian aid and economic support for Gaza could create a more favorable environment for peace talks. This approach would involve immediate relief efforts and long-term rebuilding plans.
Recent Developments and Updates
As of August 2024, the situation in Gaza remains fluid. Recent reports indicate that sporadic clashes continue, and humanitarian conditions are deteriorating. Efforts to broker a ceasefire are ongoing, with international organizations pushing for renewed negotiations.
Key Updates:
- August 2024: The UN has launched an emergency relief operation in Gaza, providing essential supplies to affected areas.
- August 2024: Peace talks are set to resume in Cairo with additional international mediators involved in the process.
Timeline of Key Events
- January 2024: The conflict between Hamas and Israeli forces intensifies, leading to significant casualties and damage.
- February 2024: Initial ceasefire talks are held, with limited progress made.
- March 2024: The US-led ceasefire negotiations in Cairo propose new conditions focusing on humanitarian aid and reconstruction.
- April 2024: Hamas rejects the proposed conditions, citing dissatisfaction with the terms and lack of progress.
- August 2024: Recent updates include ongoing clashes and emergency relief operations by the UN.
Expert Opinions: Insights from Key Figures
- Dr. Hanan Ashrawi, Palestinian Political Analyst: “The rejection of the ceasefire conditions highlights the deep-seated issues that remain unaddressed. A more inclusive approach is needed to achieve a lasting resolution.”
- Dr. Hisham Ramadan, Middle East Conflict Expert: “Hamas’s stance reflects a broader skepticism about the effectiveness of international mediation. Effective peace talks must address both security and humanitarian concerns comprehensively.”
- John Kerry, Former US Secretary of State: “The current impasse underscores the need for sustained international pressure and innovative diplomatic solutions to break the deadlock.”
Conclusion
The rejection of the new ceasefire conditions proposed in the US-led talks marks a significant development in the Gaza conflict. As the situation continues to evolve, it is crucial for all parties to engage in constructive dialogue and seek a resolution that addresses the core issues at stake. The international community’s role in supporting humanitarian efforts and facilitating peace talks will be pivotal in shaping the future of the Gaza Strip.
For Regular News and Updates Follow – Sentinel eGazette
External Sources
FAQs
Q1: What are the main reasons behind Hamas’s rejection of the ceasefire conditions?
Hamas rejected the ceasefire conditions due to perceived bias, dissatisfaction with previous agreements, and internal political pressures.
Q2: What are the proposed conditions of the new ceasefire talks?
The new ceasefire conditions propose unrestricted humanitarian aid access, comprehensive monitoring mechanisms, and frameworks for economic reconstruction in Gaza.
Q3: How has the international community responded to the rejection of the ceasefire conditions?
The international community, including the UN and the EU, has expressed concern and called for renewed dialogue and increased diplomatic efforts.
Q4: What are the potential risks of the ongoing conflict in Gaza?
The potential risks include further escalation of violence, prolonged humanitarian crises, and increased regional instability.
Q5: What steps could lead to a resolution of the Gaza conflict?
Potential steps include a revised negotiation framework, increased diplomatic engagement, and a focus on humanitarian aid and economic support.