Timeline of Youth Unemployment Trends
2009-2010: The Impact of the Global Financial Crisis
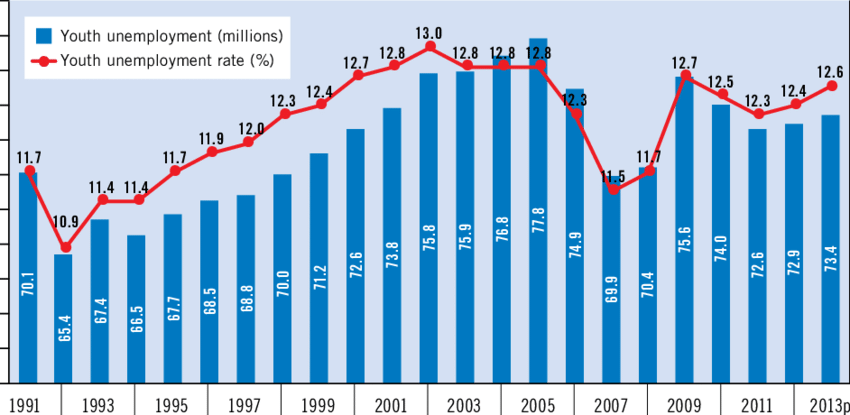
The global financial crisis of 2008-2009 had a profound effect on global youth unemployment rates. As economies around the world plunged into recession, young people were among the hardest hit. According to the International Labour Organization (ILO), youth unemployment rates soared to unprecedented levels during this period. This was due to the massive job losses in various sectors and the difficulty young job seekers faced in entering a shrinking job market.
2015-2016: Stabilization and Gradual Recovery
By 2015, many economies had started to recover from the recession, leading to a gradual stabilization in youth unemployment rates. The global economy showed signs of recovery with increased job creation and economic growth. During this period, several countries introduced policies aimed at improving job prospects for young people. Initiatives such as job training programs and internships helped mitigate the impact of unemployment among youth.
2020-2021: Pandemic-Induced Challenges
The COVID-19 pandemic caused a significant disruption in the labor market, with youth unemployment rates again rising due to widespread job losses and economic shutdowns. According to a report by the ILO in August 2020, young workers were disproportionately affected by the pandemic, with many experiencing temporary layoffs or reductions in working hours. Governments worldwide implemented various stimulus measures to support businesses and workers, which helped cushion the impact but did not fully alleviate the challenges faced by young job seekers.
2023-2024: Rebounding to a Historic Low
The most recent data from the ILO, released in August 2024, shows that global youth unemployment has reached its lowest level in 15 years. This significant improvement reflects a combination of economic recovery, effective policy interventions, and structural changes in the job market. For example, the rise in digital and green jobs has created new opportunities for young people, contributing to the decline in unemployment rates.
Expert Opinions on Youth Unemployment Trends
Dr. Manuela Tomei, Director of the ILO’s Gender, Equality, and Diversity Department, commented on the recent findings: “The reduction in youth unemployment is a testament to the resilience of young people and the effectiveness of targeted policy measures. However, it is crucial to continue supporting young workers through skills development and job creation initiatives to ensure sustained progress.”
Professor John Schmitt, a labor economist at the Center for Economic and Policy Research, also weighed in: “While the decline in youth unemployment is encouraging, we must remain vigilant. The job market is evolving rapidly due to technological advancements, and it is essential that educational systems adapt to these changes to better prepare young people for the future.”
Understanding the Decline in Youth Unemployment
Youth Unemployment Rate Drops to New Lows
The ILO’s recent report highlights that the global youth unemployment rate has dropped to its lowest level since 2009. This achievement is the result of various factors, including robust economic recovery, shifts in labor market dynamics, and proactive policy measures aimed at supporting young job seekers. The youth unemployment rate, which had peaked during previous economic downturns, now reflects a more resilient labor market for young people.
Economic Recovery and Job Creation
The recovery of the global economy post-pandemic has played a crucial role in reducing youth unemployment rates. As businesses reopened and economic activities resumed, there was a notable increase in job creation across multiple sectors. According to a 2023 report by the World Bank, global GDP growth reached 4.5% in 2023, driving job creation and reducing unemployment rates. This economic rebound has been particularly beneficial for younger workers, who have been able to re-enter the job market more easily.
Policy Interventions and Support Programs
Governments and international organizations have implemented various policies to address youth unemployment. These include job training programs, apprenticeships, and reforms in education to better align with labor market needs. For example, the European Union launched the Youth Guarantee program, which aims to provide young people with job opportunities or further education within four months of leaving school. Similarly, the U.S. Department of Labor’s Job Corps program offers training and employment services to young individuals across the country.
Regional Variations in Youth Unemployment
Asia-Pacific Region: A Beacon of Progress
In the Asia-Pacific region, countries like India and China have witnessed significant improvements in youth unemployment rates. Economic growth in these countries has been driven by investments in infrastructure, technology, and manufacturing. According to a 2024 report by the Asian Development Bank, India’s GDP growth reached 6.5% in 2024, creating new job opportunities for young people. China’s focus on technological innovation and digital industries has also contributed to this positive trend.
Sub-Saharan Africa: Challenges and Opportunities
Sub-Saharan Africa continues to face challenges related to youth unemployment despite some progress. High population growth rates and limited economic diversification have contributed to persistent unemployment issues. However, initiatives such as the African Development Bank’s Jobs for Youth in Africa program are working to address these challenges by promoting entrepreneurship and vocational training.
Europe and North America: Stability and Recovery
In Europe and North America, youth unemployment rates have stabilized, reflecting a recovery in labor markets and the effectiveness of various policy measures. The European Union’s Recovery and Resilience Facility has supported job creation and economic growth across member states. In the United States, the Biden administration’s focus on infrastructure investment and job creation has contributed to a stable labor market for young people.
Future Outlook and Implications
Sustaining the Positive Trend
The continued decline in youth unemployment is expected to be influenced by ongoing economic recovery, technological advancements, and evolving labor market trends. According to a 2024 report by McKinsey & Company, the rise of digital and green jobs will play a crucial role in shaping the future of youth employment. Policymakers, businesses, and educational institutions must collaborate on strategies to address emerging challenges and capitalize on new opportunities.
The Role of Technology and Innovation
Technological advancements are reshaping the job market, creating new opportunities for young people. The rise of artificial intelligence, data analytics, and digital communication has increased demand for skills related to these fields. Preparing young people for these emerging sectors will be essential in ensuring they remain competitive in the job market. Programs that focus on coding, data science, and digital marketing are becoming increasingly important in this context.
Educational Reforms and Skills Development
Educational reforms that align with labor market needs are crucial for sustaining the reduction in youth unemployment. According to a 2024 UNESCO report, integrating vocational training and industry-relevant skills into educational curricula can better prepare young people for the workforce. Partnerships between businesses and educational institutions can help bridge the gap between academic learning and practical job skills, ensuring that young people are equipped to meet the demands of the evolving job market.
Conclusion
The recent decline in global youth unemployment to its lowest level in 15 years is a significant achievement and a positive indicator for the future of work. This trend reflects a combination of economic recovery, effective policy measures, and structural changes in the job market. Continued efforts to adapt to evolving labor market dynamics, embrace technological advancements, and enhance educational outcomes will be crucial in sustaining and building upon this progress.
Timeline and Future Projections
2009-2010: Global youth unemployment rates spike due to the financial crisis.
2015-2016: Rates stabilize with gradual economic recovery and job creation initiatives.
2020-2021: Pandemic-induced job losses lead to a temporary increase in youth unemployment.
2023-2024: Youth unemployment reaches its lowest level in 15 years, driven by economic recovery and effective policy interventions.
In summary, while challenges remain, the current trends provide a hopeful outlook for the future of youth employment. By continuing to address the needs of young workers and adapting to the evolving job market, we can ensure that the positive momentum is sustained and further strengthened.
Sources and Further Reading
- International Labour Organization (ILO) – Global Employment Trends for Youth 2024
- World Bank – Global Economic Prospects Report 2023
- Asian Development Bank – Asia Development Outlook 2024
- McKinsey & Company – The Future of Work: Trends and Predictions
For Regular News and Updates Follow – Sentinel eGazette
FAQs
Q1: What are the primary factors contributing to the decline in global youth unemployment?
The primary factors include economic recovery post-pandemic, effective policy interventions, job creation in new sectors, and educational reforms aligning with labor market needs.
Q2: How do regional variations affect global youth unemployment rates?
Regional variations are influenced by local economic conditions, investment in industries, and government policies. For example, the Asia-Pacific region benefits from rapid economic growth, while Sub-Saharan Africa faces challenges due to high population growth and limited economic diversification.
Q3: What role do technology and innovation play in shaping future youth employment?
Technology and innovation create new job opportunities and demand for digital skills. Emerging fields such as artificial intelligence and data analytics are expected to drive future job creation, making it crucial for young people to acquire relevant skills.
Q4: How can educational reforms improve youth employment outcomes?
Educational reforms that incorporate vocational training, industry-relevant skills, and practical job experience can better prepare young people for the workforce, bridging the gap between academic learning and job market requirements.
Q5: What future trends might impact global youth unemployment?
Future trends include the rise of green jobs, digital transformation, and changes in labor market dynamics due to technological advancements. Adapting to these trends will be essential for sustaining positive youth employment outcomes.