Introduction: Germany Mortality Rate
Germany, renowned for its efficiency and innovation, faces unique challenges in its mortality landscape. While the nation enjoys a high standard of living and advanced healthcare, its mortality rate offers a mirror to the demographic shifts and health trends shaping its future. Let’s explore Germany’s mortality rate in greater depth, with expanded insights, expert opinions, and a timeline of critical events that underscore its implications.
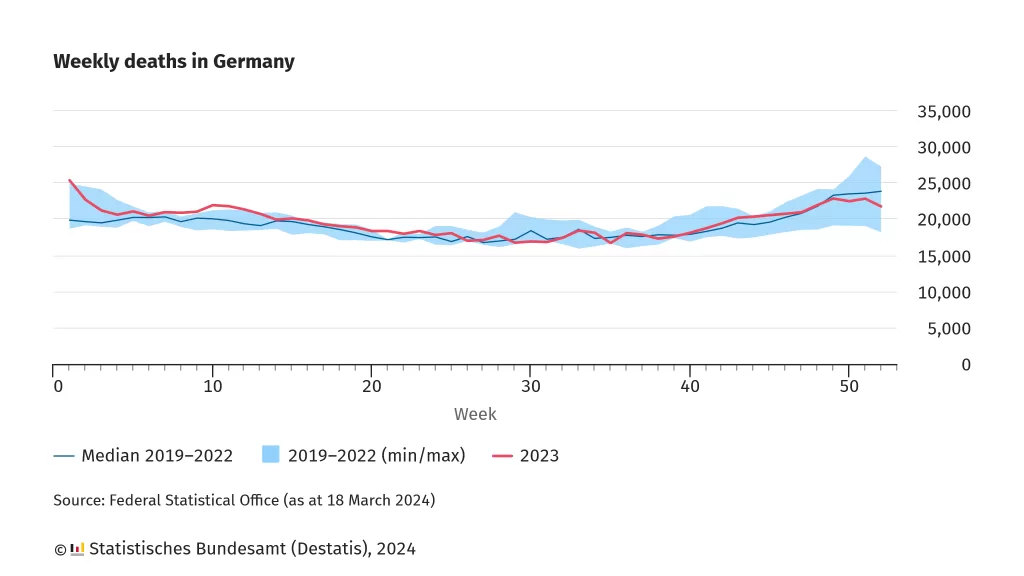
Mortality Rate in Germany: A Comprehensive Overview
Mortality rate measures the number of deaths in a population over a specified period, often per 1,000 people annually. For Germany, this figure reflects a complex interplay of aging, healthcare advances, and societal factors.
Recent statistics indicate that Germany’s mortality rate is approximately 11.4 deaths per 1,000 people as of 2023. This relatively high rate compared to global averages is influenced by a significant aging population, which accounts for a substantial portion of deaths.
Understanding these dynamics is vital for addressing healthcare challenges, planning policy interventions, and preparing for future socio-economic shifts.
Key Trends in Germany’s Mortality Rate
1. The Aging Population Phenomenon
Germany’s population dynamics are heavily skewed toward older age groups. Over 22% of the population is aged 65 or older, and projections suggest this proportion will rise in the coming decades.
- Implications of Aging:
- Increased prevalence of age-related illnesses such as dementia and osteoporosis.
- Higher demand for geriatric care facilities and specialists.
- Economic pressures due to a shrinking workforce and growing pension liabilities.
2. Life Expectancy Variances
Germany boasts an average life expectancy of 81 years, with women typically living longer (83 years) than men (79 years). While life expectancy has steadily increased over the decades, challenges like the COVID-19 pandemic temporarily disrupted this trend.
3. Pandemic Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic significantly altered mortality trends, particularly in 2020 and 2021, when the virus claimed over 100,000 lives. This unprecedented health crisis highlighted vulnerabilities in public health infrastructure and emphasized the importance of preventive care and pandemic preparedness.
Leading Causes of Death in Germany
An analysis of mortality causes offers valuable insights into public health priorities.
1. Cardiovascular Diseases
Heart diseases remain the leading cause of death, accounting for 40% of fatalities. Common conditions include:
- Coronary artery disease
- Heart attacks
- Strokes
Contributing Factors:
- Sedentary lifestyles
- Smoking
- Unhealthy diets
- Genetic predispositions
2. Cancer
Cancer is the second most common cause of death, responsible for nearly 25% of all fatalities. Lung, breast, and colorectal cancers are particularly prevalent, despite advancements in early detection and treatment.
3. Respiratory Diseases
Chronic respiratory conditions, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and pneumonia, are significant contributors to mortality, especially among the elderly population.
4. External Causes
While accounting for a smaller percentage of deaths, accidents, suicides, and substance abuse remain critical areas of concern.
Regional Mortality Variations: The East-West Divide
Germany’s historical division into East and West continues to influence health outcomes and mortality rates.
- Eastern Germany experiences slightly higher mortality rates, driven by lower incomes, older populations, and disparities in healthcare infrastructure.
- Urban vs. Rural Dynamics: Urban areas benefit from advanced medical facilities, while rural regions face challenges in healthcare access.
Germany’s Healthcare System and Mortality Management
Germany’s healthcare system plays a crucial role in shaping mortality trends. Its universal coverage ensures that all residents have access to medical care, regardless of income or employment status.
Strengths
- Preventive Care: Germany emphasizes early detection programs, particularly for cancer and cardiovascular diseases.
- Technological Advancements: Cutting-edge treatments and state-of-the-art medical technologies are widely available.
- Public Health Campaigns: Initiatives targeting smoking cessation, obesity reduction, and mental health awareness have gained traction.
Challenges
- Addressing mental health issues and suicide prevention.
- Ensuring equitable access to healthcare in rural regions.
- Adapting the system to meet the needs of an aging population.
Economic and Social Implications
The mortality rate has far-reaching implications for Germany’s economy and society:
- Economic Challenges
- The aging population puts pressure on pensions and healthcare spending.
- Workforce shortages may hinder economic productivity.
- Healthcare Strain
- Chronic diseases like diabetes and hypertension demand long-term care, increasing healthcare expenditures.
- Emergency preparedness remains critical in light of pandemics and climate-related health crises.
Expert Opinions on Germany’s Mortality Trends
Dr. Maria Klein-Schmeink (Healthcare Policy Analyst)
“Germany’s aging population poses unique challenges that require proactive measures. Investments in geriatric care, telemedicine, and community health initiatives are essential to address these issues effectively.”
Dr. Markus Zimmermann (Geriatrician)
“Encouraging active lifestyles among seniors can significantly reduce the risk of chronic diseases. Programs focusing on physical activity, social engagement, and balanced nutrition are critical in improving quality of life.”
Dr. Hans Becker (Public Health Specialist)
“Germany must prioritize mental health services, particularly in rural areas, to address rising cases of depression and suicide. Expanding access to therapy and counseling services is vital.”
Timeline: Significant Events Impacting Mortality in Germany
- 2015: Steady improvement in healthcare access and reduced mortality rates due to public health campaigns.
- 2020: COVID-19 pandemic causes a spike in deaths, exposing weaknesses in emergency preparedness.
- 2021-2022: Vaccination campaigns help stabilize mortality rates, with declining COVID-related deaths.
- 2023: Germany continues to focus on preventive care and managing the healthcare needs of an aging population.
Conclusion
Germany’s mortality rate serves as a reflection of its demographic trends, healthcare advancements, and societal challenges. While progress in healthcare and life expectancy is commendable, the country faces pressing issues related to its aging population and chronic diseases. Policymakers, healthcare providers, and communities must collaborate to ensure a healthier future for all citizens. By addressing disparities, investing in innovative care, and fostering public health awareness, Germany can navigate these challenges and continue to thrive.
📚 Take Your Trading And Financial Skills to the Next Level!
If you enjoyed this post, dive deeper with our Profitable Trader Series—a step-by-step guide to mastering the stock market.
- Stock Market 101: Profits with Candlesticks
- Stock Market 201: Profits with Chart Patterns
- Stock Market 301: Advanced Trade Sheets
Start your journey now!
👉 Explore the Series Here
For Regular News and Updates Follow – Sentinel eGazette
FAQs:
1. What factors contribute to Germany’s aging population?
Germany’s aging population is influenced by declining birth rates, longer life expectancy, and improved healthcare standards.
2. How does Germany address disparities in healthcare access?
Germany uses universal healthcare, public health campaigns, and rural health initiatives to minimize disparities.
3. What steps is Germany taking to reduce cardiovascular deaths?
Germany promotes early detection programs, healthier lifestyle choices, and access to advanced cardiac treatments.
4. How has the COVID-19 pandemic impacted mortality trends in Germany?
The pandemic caused a spike in deaths in 2020-2021 but highlighted the importance of vaccination, healthcare preparedness, and public awareness.
5. Why do Eastern regions in Germany have higher mortality rates?
Eastern regions face higher mortality rates due to aging populations, lower incomes, and historical healthcare disparities.